Reverse Engineering Methods Rich in Variations
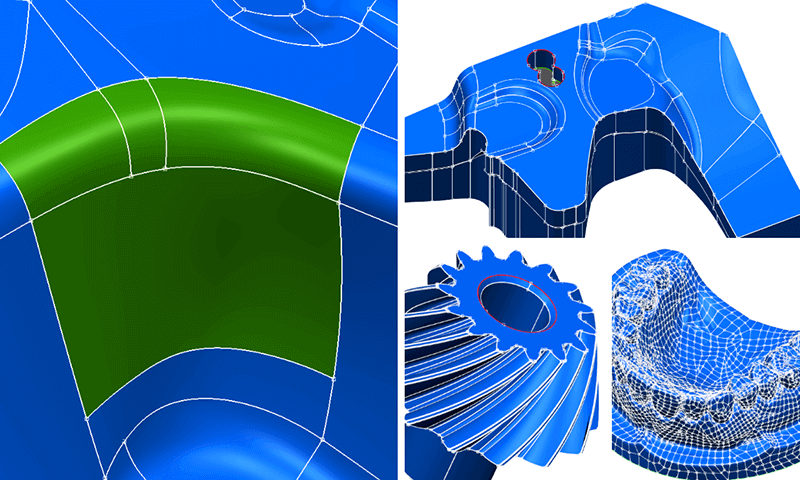
spScan provides several reverse engineering methods as standard tools.
You can select from a variety of methods depending on the application and purpose for reverse engineering, including the patch surface configuration method, which creates prototype surfaces automatically from the point cloud; a method of creating CAD surface configurations that are easy to use in later processes; and the partial reverse engineering method, which takes a short amount of time to repair only the errors compared to the CAD data.
Reverse engineering methods using spScan
spScan now provides the following six reverse engineering methods as standard tools.
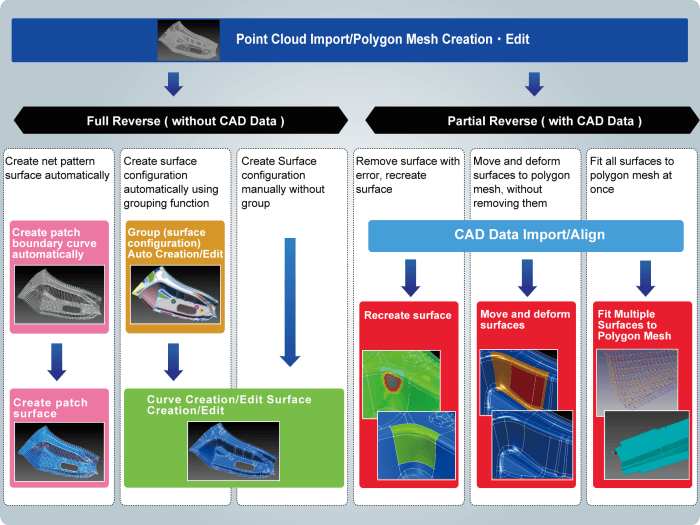
- Total reverse engineering: A reverse engineering method that uses only the point cloud data to create the CAD spline surfaces.
- Patch spline surface creation method: ‘Automatic Patch Creation’
- A reverse engineering method that creates CAD spline surfaces for patch (4-sided net pattern) surface configurations.
- Automatic prototype surface creation method: ‘Automatic Fillet Creation’
- A reverse engineering method that uses the grouping function to create simple CAD spline surfaces automatically. It is under development for improvement.
- Manual CAD composition surface creation method: ‘Manual Fillet Creation’
- A reverse engineering method that allows creation of spline surface configurations equivalent to the CAD data manually.
- Patch spline surface creation method: ‘Automatic Patch Creation’
- Partial reverse engineering: A reverse engineering method that uses both the point cloud data and CAD data to create CAD spline surfaces containing errors only.
- Partial reverse engineering
- Recreate CAD spline surfaces containing only errors between the point cloud and the CAD data.
- Creating spline surfaces containing only errors allows reduction of man-hours required in the reverse engineering.
- Spline surface optimization and spline surface fitting
- Create CAD spline surfaces by moving and deforming CAD spline surfaces containing errors to fit them to the point cloud.
- Spline surface optimization allows spline surface configurations to be maintained during the move.
- This can reduce the man-hours required in the reverse engineering.
- Multiple spline surface fitting
- Create CAD spline surfaces through batch auto process of multiple CAD spline surfaces to fit them to the point cloud.
- This can greatly reduce the man-hours required in the reverse engineering.
- The spline surfaces of defective portions need to be modified because it is impossible to maintain continuity between surfaces after fitting under certain circumstances.
- Partial reverse engineering
Types of reverse engineering surfaces in spScan
spScan offers several types of reverse engineering surfaces. You can select the type of reverse engineering surface depending on your purpose and intended application.
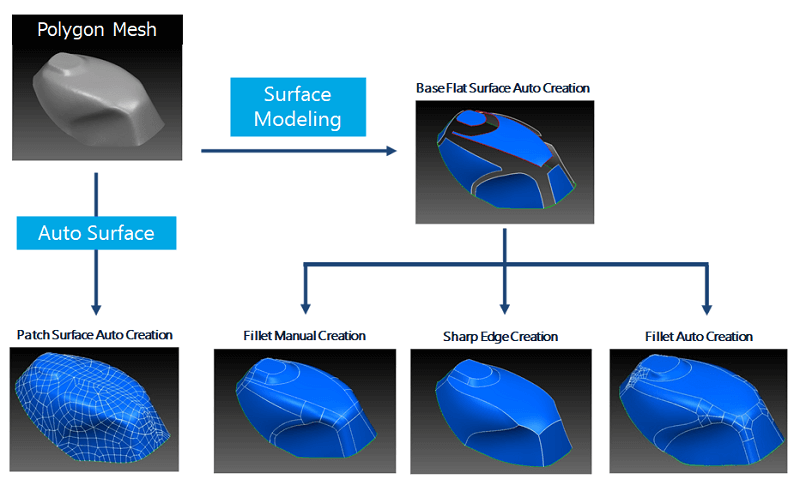
- Automatic patch creation
- Create patch surfaces (four-sided net pattern surface configurations) from the polygon mesh.
- Because bumpy polygon mesh shapes will affect the quality of the created surface, it is important to edit the polygon mesh for fill holes, shape smoothing, etc.
- This method can greatly reduce man-hour for surface creation compared with other reverse engineering surfaces.
- It is suitable for applications where the reverse engineered surface data is directly used to medical reverse engineering, the creation of art object replicas, and so on.
- It can be used as reverse engineered data for 3-Dimensional printers.
- If the reverse engineered surfaces need to be edited, the surfaces will need to be recreated or edited by a separate CAD program.
- Manual fillet creation
- A typical reverse engineered surface configuration in spScan enables the creation of surfaces with surface configurations identical to CAD.
- After creating surfaces (basic flat surfaces) in a location with a large curvature radius, fillet shapes are manually created between the basic flat surfaces.
- With spScan, we continue to develop tools that simplify manual operation even further by improving operability and adding automatic processing and other specialized tools.
- When you create spline surfaces, you can easily control whether to prioritize accuracy of recreating the point cloud or to prioritize the quality of the reverse engineered surfaces.
- Used together with partial reverse engineering methods, these tools can greatly reduce reverse engineering man-hours.
- Sharp edge creation
- spScan can create smooth basic flat surfaces resulting in a sharp edge (intersections between base surfaces).
- As with general CAD modeling methods, the fillet surface with a specified radius can be created after the sharp edges were created.
- Automatic fillet creation
- With spScan, we aim to automate fillet creation in order to reduce mon-hour for the manual operation.
- Currently, automatic fillet creation is still in the development phase, but we continue to develop tools enabling automatic creation of surface configurations identical to manual fillet creation.
tag : Reverse engineering methods Reverse engineered surface types
